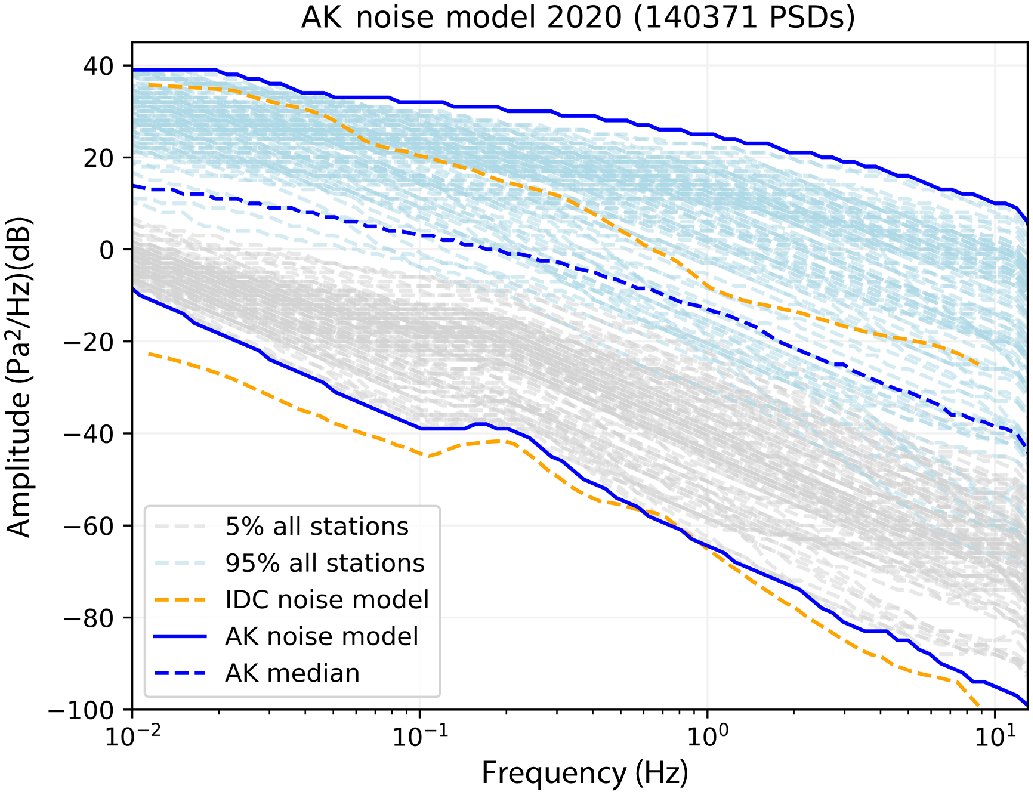
The addition of 108 infrasound sensors—a legacy of the temporary USArray Transportable Array (TA) deployment—to the Alaska regional network provides an unprecedented opportunity to quantify the effects of a diverse set of site conditions on ambient infrasound noise levels. TA station locations were not chosen to optimize infrasound performance, and consequently span a dramatic range of land cover types, from temperate rain forest to exposed tundra. In this study, we compute power spectral densities for 2020 data and compile new ambient infrasound low‐ and high‐noise models for the region. In addition, we compare time series of root‐mean‐squared (rms) amplitudes with wind data and high‐resolution land cover data to derive noise–wind speed relationships for several land cover categories. We observe that noise levels for the network are dominated by wind, and that network noise is generally higher in the winter months when storms are more frequent and the microbarom is more pronounced. Wind direction also exerts control on noise levels, likely as a result of infrasound ports being systematically located on the east side of the station huts. We find that rms amplitudes correlate with site land cover type, and that knowledge of both land cover type and wind speed can help predict infrasound noise levels. Our results show that land cover data can be used to inform infrasound station site selection, and that wind–noise models that incorporate station land cover type are useful tools for understanding general station noise performance.

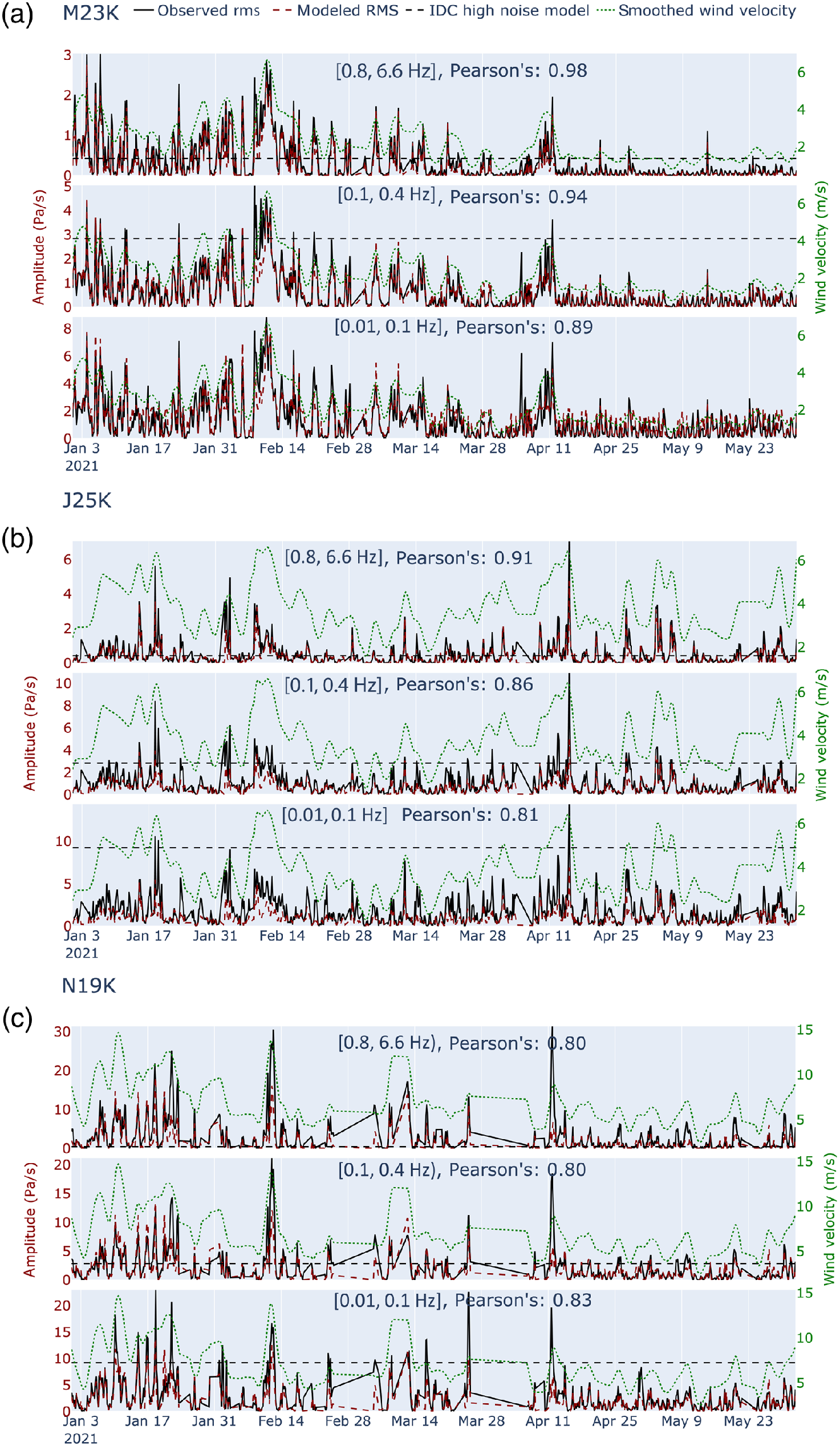
![(a) RMS amplitude time series in the [0.8, 6.6] Hz passband for all the 104 stations for 2020. Traces are organized vertically by the latitude of each station. Similar figures for the [0.01, 0.1], and [0.1, 0.4] Hz passbands are provided in the Appendix, although general trends are similar. Amplitudes have been normalized across the network. (b) Time series of circles scaled by the residual of fitting a line to the hourly PSD in the [0.1, 0.4] Hz passband for 2020. Larger dots represent time periods when t](/sites/default/files/2022-05/rms.png)
![Root‐mean‐squared (rms) infrasound amplitude for 2020 binned by station land cover for the [0.8, 6.6] Hz passband. The upper and lower edges of the boxes denote the third and first quartiles, respectively. The horizontal line in each box denotes the medians, whereas the means are shown by white circles. The bars extend to 1.5 times the interquartile range. For clarity, outliers are not plotted. Boxes are colored by mean wind speed categories from the 2020 data.](/sites/default/files/2022-05/boxes.png)
![Two‐dimensional histograms showing relationships between observed wind speed and rms noise for 2020. The bins have been normalized to indicate the density of observations in each bin, with warmer colors indicating more observations. The top row is sites in the exposed land cover category, middle row is partially exposed, and bottom row is sheltered sites. The columns show the three passbands: [0.01, 0.1], [0.1, 0.4], and [0.8, 6.6] Hz. The smoothed median for each dataset is shown by cyan circles, the 5th a](/sites/default/files/2022-05/wn_models.png)